Research Highlights
Research Highlights
A selection of highlights culled from publications by HAO staff.
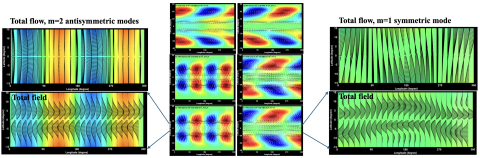
Magnetohydrodynamic Instabilities of Double Magnetic Bands in a Shallow-water Tachocline Model: II Teleconnection Between High- and Low-latitude Bands and Across Equator
Mausumi Dikpati, Bernadett Belucz, Robertus Erdelyi, Peter A Gilman, Scott W McIntosh and Breno Raphaldini find that latitude-location, latitude-separation, and amplitude of the toroidal magnetic field bands strongly influence the latitudinal structure and growth rates of the unstable modes, of both symmetries about the equator. These properties can lead to 'teleconnections' between low- and high-latitudes in each hemisphere and across the equator.
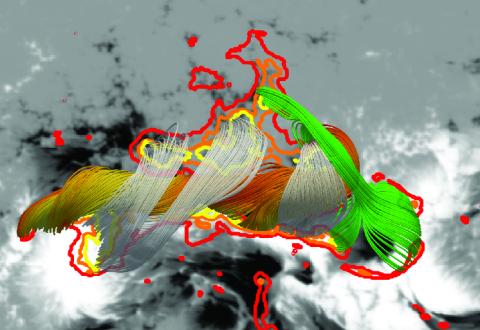
Magnetic Field Evolution of the Solar Active Region 13664
Robert Jarolim, Astrid M. Veronig, Stefan Purkhart, Peijin Zhang, and Matthias Rempel provide a detailed record of the magnetic field evolution of AR 13664, now publicly available for further research. Their results show that drops in free magnetic energy coincide with large solar flares, and that all modeled X-class flares were associated with a sudden decrease in magnetic energy.
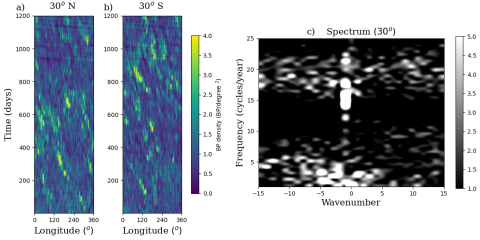
Spectra of solar shallow-water waves from bright point observations
Breno Raphaldini, Mausumi Dikpati, Scott W. McIntosh, and Andre S. W. Teruya, utilize 3 years of global, synchronous observations of coronal bright point densities to obtain empirical signatures of dispersion relations that can be attributed to the simulated waves in tachocline. By tracking the bright point densities at selected latitudes, they compute their wave-number X frequency spectra.
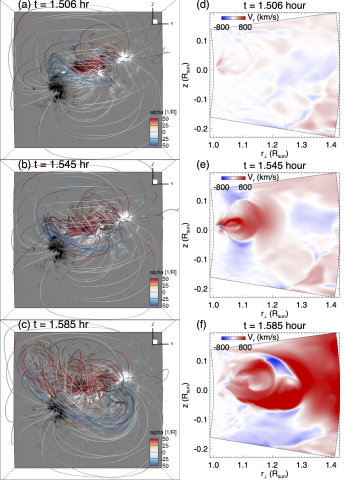
A data-driven MHD simulation of the 2011-02-15 coronal mass ejection from Active Region NOAA 11158
Yuhong Fan, Maria Kazachenko, Andrei Afanasev, and George Fisher present a boundary data-driven magneto-hydrodynamic (MHD) simulation of the 2011-02-15 coronal mass ejection (CME) event of Active Region (AR) NOAA 11158. The simulation is driven at the lower boundary with an electric field derived from the normal magnetic field and the vertical electric current measured from the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) Helioseismic Magnetic Imager (HMI) vector magnetograms.
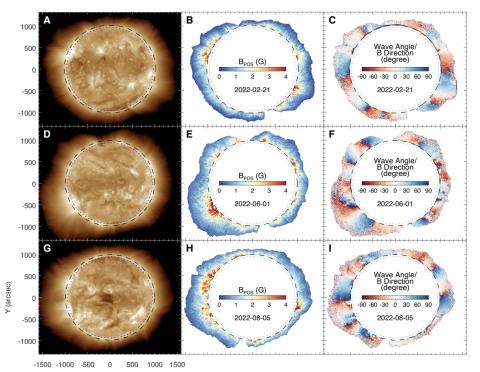
Observing the evolution of the Sun’s global coronal magnetic field
Zihao Yang, Hui Tian, Steven Tomczyk, Xianyu Liu, Sarah Gibson, Richard Morton, Cooper Downs, using the Upgraded Coronal Multi-channel Polarimeter, have obtained magnetograms of the global corona above the solar limb over approximately eight months.
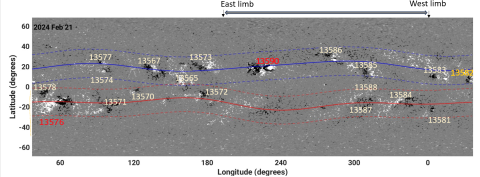
Global and Local Dynamics of X-flare Producing Active Regions During Solar Cycle 25 Peak-Phase
Breno Raphaldini, Mausumi Dikpati, Andre S. W. Teruya , Kiran Jain, Aimee A. Norton , and Scott W. McIntosh investigate the circumstances under which two of the most flare-prolific active regions of solar cycle 25, namely ARs 13590 and 13514, flared.
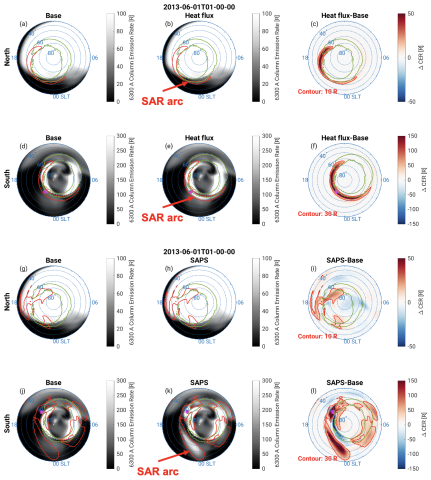
SubAuroral Red Arcs Generated by Inner Magnetospheric Heat Flux and by SubAuroral Polarization Streams
Dong Lin, Wenbin Wang, Mei-Ching Fok, Kevin Pham, Jia Yue, and Haonan Wu, utilize first-principles inner magnetosphere model and ionosphere-thermosphere model to illustrate the thermodynamic coupling effects between the topside ionosphere and the magnetosphere, and compare the relative significance between the heat flux and plasma convection due to electrodynamic coupling.

EUV polarimetric diagnostics of the solar corona: the Hanle effect of Ne viii 770 A
Raveena Khan, Sarah Gibson, Roberto Casini, and K. Nagaraju utilize 3D 'Magneto-hydrodynamic Algorithm outside a Sphere' (MAS) models as input to the FORWARD code to model polarization in Ne viii line produced due to resonance scattering, and interpret its modification due to collisions and the magnetic fields through the Hanle effect.
On the intermittency of hot plasma loops in the solar corona
P. Judge and N.P.M. Kuin ask why and how are entire hydromagnetic structures only intermittently loaded with bright coronal plasma in the Sun? Their findings consolidate the claim that unobserved physical processes are at work which govern the heating of long-lived coronal loops.