Research Highlights
Research Highlights
A selection of highlights culled from publications by HAO staff.
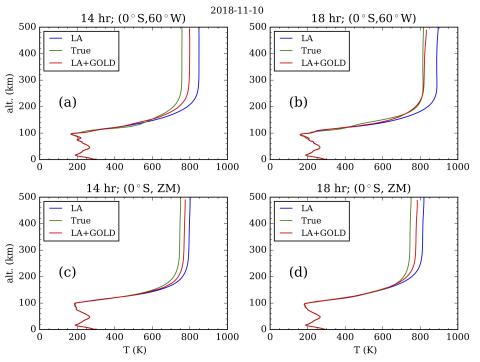
Impact of GOLD Retrieved Thermospheric Temperatures on a Whole Atmosphere Data Assimilation Model
The present investigation evaluates the assimilation of synthetic data which has properties similar to actual Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk (GOLD) level-2 (L2) and other conventional lower atmospheric observations. The lower atmospheric and GOLD L2 temperature (Tdisk) are assimilated in the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model with thermosphere-ionosphere eXtension (WACCMX) using Data Assimilation Research Testbed (DART).
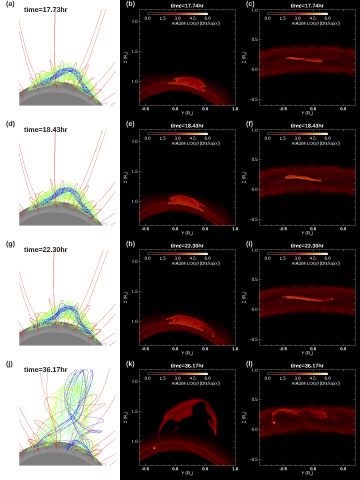
Simulations of prominence eruption preceded with large amplitude longitudinal oscillations and draining
We present magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) simulations of the evolution from quasi-equilibrium to eruption of a prominence-forming twisted coronal flux rope under a coronal streamer. The prominence condensations form at the dips of the twisted flux rope due to run-away radiative cooling.
Sudden Stratospheric Warmings
Sudden stratospheric warmings (SSWs) are impressive fluid dynamical events in which large and rapid temperature increases in the winter polar stratosphere (∼10–50km) are associated with a complete reversal of the climatological wintertime westerly winds.
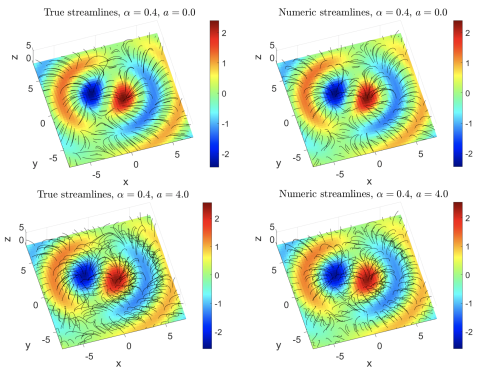
Reconstructing the Coronal Magnetic Field: The Role of Cross-Field Currents in Solution Uniqueness
We present a new 3D magnetohydrostatic (MHS) direct elliptic solver for extrapolating the coronal magnetic field from photospheric boundary conditions in a manner consistent with an assumed plasma distribution.
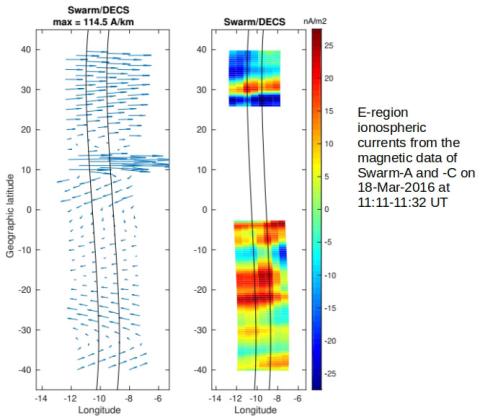
Dipolar elementary current systems for ionospheric current reconstruction at low and middle latitudes
The flow of ionospheric current can be probed by examining magnetic field measurements at the ground and at Low-Earth-Orbit (LEO) altitude. The interpretation of the magnetic field perturbations with respect of ionospheric current flow is complicated by the fact that the perturbations reflect the integrated effect of current flow close-by and far-away.

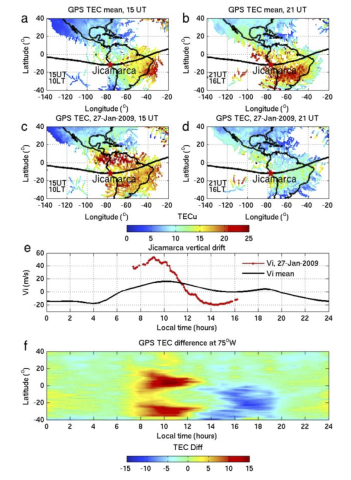
Formation of Double Tongues of Ionization During the 17 March 2013 Geomagnetic Storm
During geomagnetic disturbances, enhanced high‐latitude convection transports ionospheric F2‐region plasma from the dayside midlatitude region into the polar cap, leading to structures such as tongues of ionization (TOIs) and patches. In this study, we investigate the dynamic evolution of TOIs during the 17 March 2013 storm using a high‐resolution coupled thermosphere‐ionosphere‐electrodynamics model and Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellite observations.
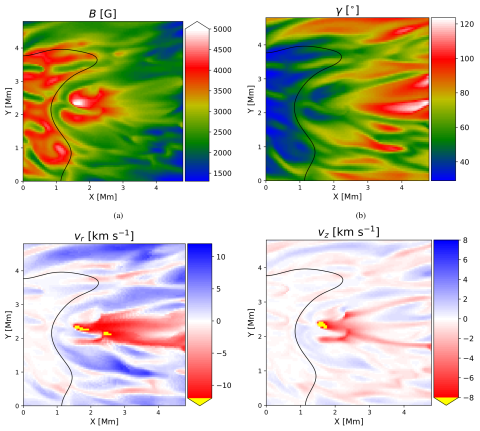
Superstrong photospheric magnetic fields in sunspot penumbrae
Recently, there have been some reports of unusually strong photospheric magnetic fields (which can reach values of over 7 kG) inferred from Hinode SOT/SP sunspot observations within penumbral regions. These superstrong penumbral fields are even larger than the strongest umbral fields in record and appear associated with supersonic downflows.
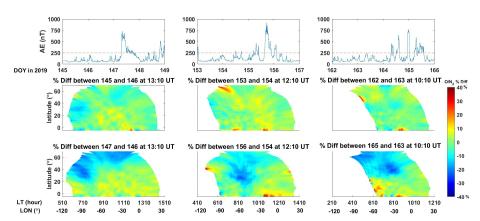
The 2‐D Evolution of Thermospheric ∑O/N2 Response to Weak Geomagnetic Activity During Solar‐Minimum Observed by GOLD
We conduct observational and modeling studies of thermospheric composition responses to weak geomagnetic activity (non-geomagnetic storms).
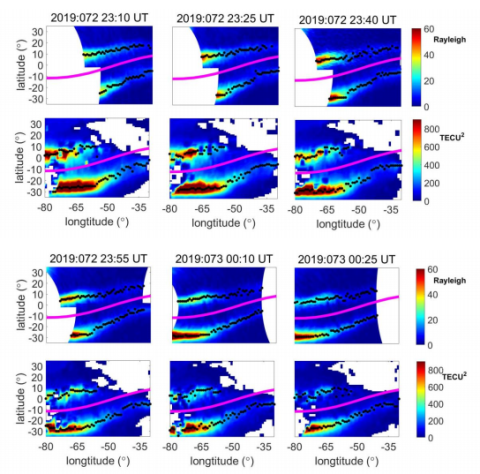
Comparison of GOLD nighttime measurements with total electron content: preliminary results
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Global‐scale Observations of the Limb and Disk (GOLD) has been imaging the thermosphere and ionosphere since October 2018. It provides continuous measurements over a large area from its geostationary orbit.