Research Highlights
Research Highlights
A selection of highlights culled from publications by HAO staff.
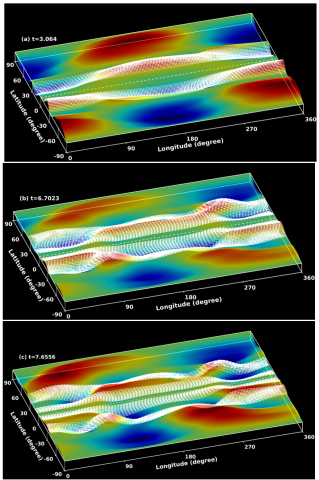
Dynamical Splitting Of A Spot-producing Magnetic Ring In A Nonlinear Shallow-water Model
We explore the fundamental physics of narrow toroidal rings during their nonlinear magnetohydrodynamic evolution at tachocline depths.
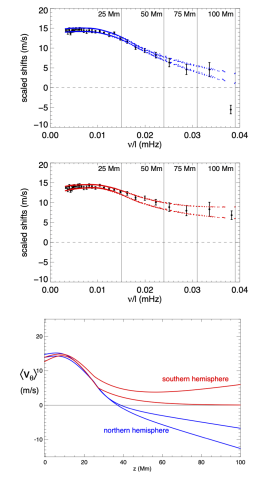
Probing the Solar Meridional Circulation using Fourier Legendre Decomposition
We apply the helioseismic methodology of Legendre Function Decomposition to 88 months of Dopp- lergrams obtained by the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) as the basis of inferring the depth variation of the mean meridional flow, as averaged between 20 and 60 degrees latitude and in time, in both the northern and southern hemispheres.
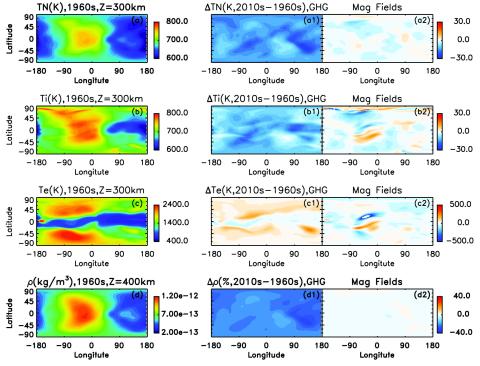
Climate Changes in the Upper Atmosphere: Contributions by the Changing Greenhouse Gas Concentrations and Earth's Magnetic Field From the 1960s to 2010s
Previous studies have established the importance of the increasing greenhouse gas concentrations in causing trends in the thermosphere and ionosphere (T-I). Recent work indicates that the changing Earth’s magnetic field is also important. We conduct whole atmosphere model simulations to examine T-I trends driven by these two drivers and their relative importance.
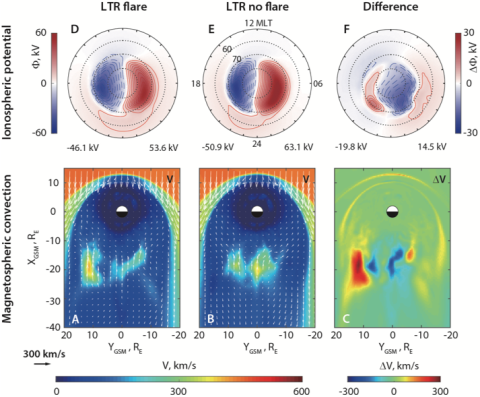
Geospace response to an extreme solar flare
Solar flares—a sudden eruption of electromagnetic radiation at the Sun—are known to have significant impacts on Earth’s upper atmosphere and ionosphere, but their collective effects on geospace as an integrated system have never been examined.
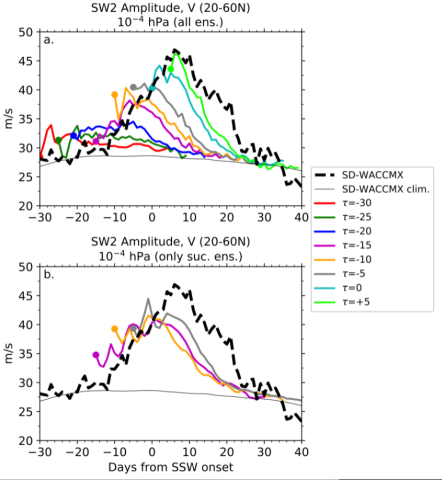
Predictability of the Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere during Major Sudden Stratospheric Warmings
Stratosphere sudden warmings (SSWs) are strong disturbances in the high latitude, wintertime, stratospheric polar vortex. The effects of SSWs are, however, not limited to the stratosphere, and SSWs influence the whole atmosphere, including tropospheric weather, chemistry and dynamics of the middle atmosphere, and the near-Earth space environment.
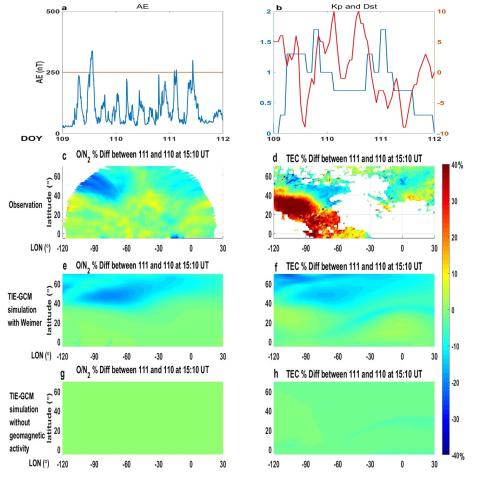
Variations in thermosphere composition and ionosphere total electron content under ‘geomagnetically quiet’ conditions at solar-minimum
We conducted observational and modeling studies of thermospheric composition and ionospheric total electron content (TEC) variations during two geomagnetically quiet periods (maximum Kp=1.7) at solar minimum.
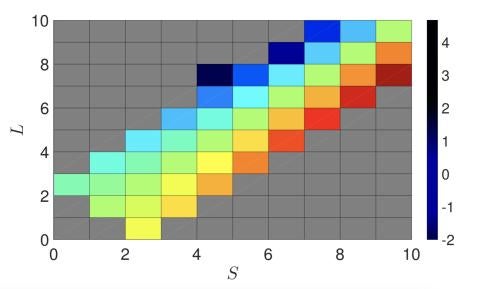
Atomic structure calculations of Land ́e g factors of astrophysical interest with direct applications for solar coronal magnetometry
We perform a detailed theoretical study of the atomic structure of ions with ns2npm ground configurations and focus on departures from LS coupling which directly affect the Land ́e g factors of magnetic dipole lines between levels of the ground terms.

Investigation of a neutral ‘tongue’ observed by GOLD during the geomagnetic storm on May 11,2019
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration Global-scale observations of the Limb and Disk (GOLD) mission observed a unique structure of thermospheric column density ratio of O to N2 (∑O/N2) during a geomagnetic storm on day of year (DOY) 130 (May 10) to DOY 132 in 2019. The percentage difference of ∑O/N2 between the storm time (DOY 131) and the quiet time (DOY 128) had a relatively enhanced ∑O/N2 region sandwiched by two depleted regions over North America and the Atlantic Ocean in the Northern Hemisphere.
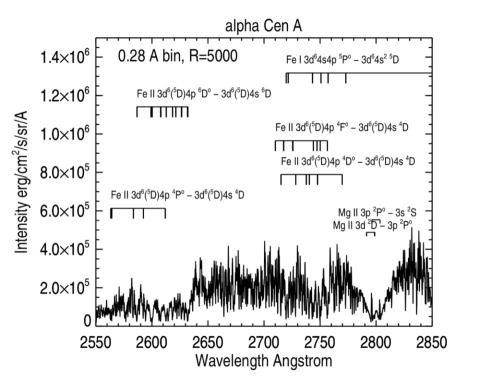
Measuring the magnetic origins of solar flares, CMEs and Space Weather
We take a broad look at the problem of identifying the magnetic solar causes of space weather. The challenges are best met through a combination of near UV lines of bright Mg II, and lines of Fe II and Fe I (mostly within the 4s − 4p transition array) which form in the chromosphere up to 20,000 K.